DE10 Advance revC demo: Users LED and KEY
From Terasic Wiki
(Created page with "This demonstration shows how to control the users LED and KEY by accessing the register of GPIO controller through the memory-mapped device driver. The memory-mapped device drive...") |
(→Function Block Diagram) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
:::[[File:Block diagram of GPIO demonstration.jpg|600px]] | :::[[File:Block diagram of GPIO demonstration.jpg|600px]] | ||
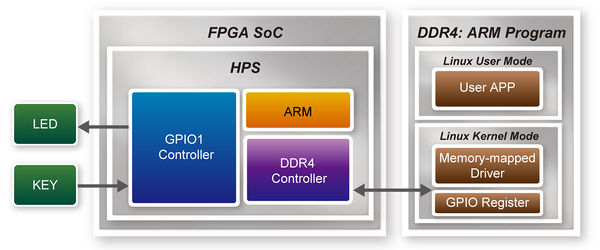
::::::::::Figure 3-1 Block diagram of GPIO demonstration | ::::::::::Figure 3-1 Block diagram of GPIO demonstration | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Block Diagram of GPIO Interface= | ||
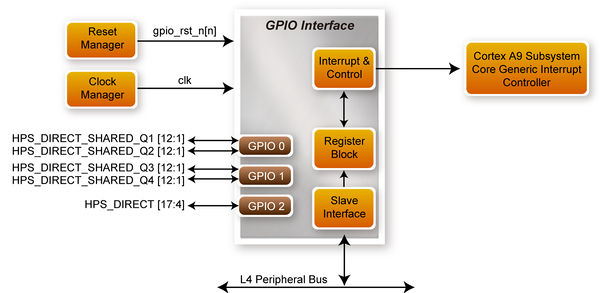
| + | The HPS provides three general-purpose I/O (GPIO) interface modules. Figure 3-2 shows the block diagram of GPIO Interface. GPIO[28..0] is controlled by the GPIO0 controller and GPIO[57..29] is controlled by the GPIO1 controller. GPIO[70..58] and input-only GPI[13..0] are controlled by the GPIO2 controller. | ||
| + | :::[[File:Block diagram of GPIO Interface.jpg|600px]] | ||
| + | :::::::::Figure 3-2 Block diagram of GPIO Interface | ||
| + | |||
| + | =GPIO Register Block= | ||
| + | The behavior of I/O pin is controlled by the registers in the register block. There are three 32-bit registers in the GPIO controller used in this demonstration. The registers are: | ||
| + | *gpio_swporta_dr: write output data to output I/O pin | ||
| + | *gpio_swporta_ddr: configure the direction of I/O pin | ||
| + | *gpio_ext_porta: read input data of I/O input pin | ||
| + | |||
| + | The gpio_swporta_ddr configures the LED pin as output pin and drives it high or low by writing data to the gpio_swporta_dr register. The first bit (least significant bit) of gpio_swporta_ddr controls the direction of first IO pin in the associated GPIO controller and the second bit controls the direction of second IO pin in the associated GPIO controller and so on. The value "1" in the register bit indicates the I/O direction is output, and the value "0" in the register bit indicates the I/O direction is input. <br/><br/> | ||
| + | The first bit of gpio_swporta_dr register controls the output value of first I/O pin in the associated GPIO controller, and the second bit controls the output value of second I/O pin in the associated GPIO controller and so on. The value "1" in the register bit indicates the output value is high, and the value "0" indicates the output value is low. <br/><br/> | ||
| + | The status of KEY can be queried by reading the value of gpio_ext_porta register. The first bit represents the input status of first IO pin in the associated GPIO controller, and the second bit represents the input status of second IO pin in the associated GPIO controller and so on. The value "1" in the register bit indicates the input state is high, and the value "0" indicates the input state is low. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =GPIO Register Address Mapping= | ||
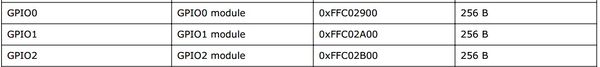
| + | The registers of HPS peripherals are mapped to HPS base address space 0xFC000000 with 64MB size. The registers of the GPIO1 controller are mapped to the base address 0xFFC02A00 with 256B size, and the registers of the GPIO2 controller are mapped to the base address 0xFFC02B00 with 256B size, as shown in Figure 3-3. <br/> | ||
| + | :::[[File:GPIO address map.jpg|600px]] | ||
| + | ::::::::::Figure 3-3 GPIO address map | ||
Revision as of 14:19, 27 August 2018
This demonstration shows how to control the users LED and KEY by accessing the register of GPIO controller through the memory-mapped device driver. The memory-mapped device driver allows developer to access the system physical memory.
Contents |
Function Block Diagram
Figure 3-1 shows the function block diagram of this demonstration. The users LED and KEY are connected to the GPIO1 controller in HPS. The behavior of GPIO controller is controlled by the register in GPIO controller. The registers can be accessed by application software through the memory-mapped device driver, which is built into Intel SoC Linux.
Block Diagram of GPIO Interface
The HPS provides three general-purpose I/O (GPIO) interface modules. Figure 3-2 shows the block diagram of GPIO Interface. GPIO[28..0] is controlled by the GPIO0 controller and GPIO[57..29] is controlled by the GPIO1 controller. GPIO[70..58] and input-only GPI[13..0] are controlled by the GPIO2 controller.
GPIO Register Block
The behavior of I/O pin is controlled by the registers in the register block. There are three 32-bit registers in the GPIO controller used in this demonstration. The registers are:
- gpio_swporta_dr: write output data to output I/O pin
- gpio_swporta_ddr: configure the direction of I/O pin
- gpio_ext_porta: read input data of I/O input pin
The gpio_swporta_ddr configures the LED pin as output pin and drives it high or low by writing data to the gpio_swporta_dr register. The first bit (least significant bit) of gpio_swporta_ddr controls the direction of first IO pin in the associated GPIO controller and the second bit controls the direction of second IO pin in the associated GPIO controller and so on. The value "1" in the register bit indicates the I/O direction is output, and the value "0" in the register bit indicates the I/O direction is input.
The first bit of gpio_swporta_dr register controls the output value of first I/O pin in the associated GPIO controller, and the second bit controls the output value of second I/O pin in the associated GPIO controller and so on. The value "1" in the register bit indicates the output value is high, and the value "0" indicates the output value is low.
The status of KEY can be queried by reading the value of gpio_ext_porta register. The first bit represents the input status of first IO pin in the associated GPIO controller, and the second bit represents the input status of second IO pin in the associated GPIO controller and so on. The value "1" in the register bit indicates the input state is high, and the value "0" indicates the input state is low.
GPIO Register Address Mapping
The registers of HPS peripherals are mapped to HPS base address space 0xFC000000 with 64MB size. The registers of the GPIO1 controller are mapped to the base address 0xFFC02A00 with 256B size, and the registers of the GPIO2 controller are mapped to the base address 0xFFC02B00 with 256B size, as shown in Figure 3-3.