Word2wiki bal gsq
From Terasic Wiki
(→{{anchor|RefHeadingToc512004893}} LEDs on the Motor Driver Board{{anchor|OLELINK38}} {{anchor|OLELINK39}}) |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | = | |
| + | = <span style="color:#000000;">Chpater1 Chapter 7</span>PCI Express Design for Windows == | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">PCI Express is commonly used in consumer, server, and industrial applications, to link motherboard-mounted peripherals. From this demonstration, it will show how the PC Windows and FPGA communicate with each other through the PCI Express interface. Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express with Avalon-MM DMA IP is used in this demonstration. For detail about this IP, please refer to Altera document [https://www.altera.com/en_US/pdfs/literature/ug/ug_a10_pcie_avmm_dma.pdf ug_a10_pcie_avmm_dma.pdf].</div> | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | === 1-0-1 7.1 PCI Express System Infrastructure === | |
| - | |||
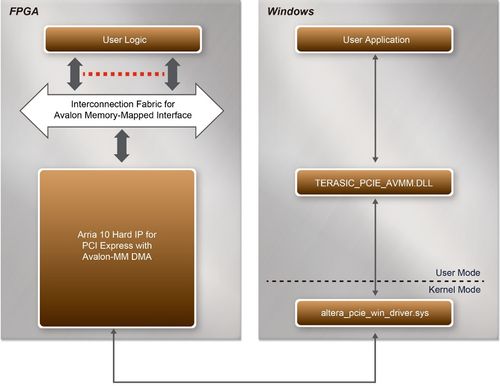
| - | + | [[#Figure71|Figure 7-1]] shows the infrastructure of the PCI Express System in this demonstration. It consists of two primary components: FPGA System and PC System. The FPGA System is developed based on Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express with Avalon-MM DMA. The application software on the PC side is developed by Terasic based on Altera’s PCIe kernel mode driver. | |
| - | :[[ | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_1.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | : | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-1 Infrastructure of PCI Express System'''</div> |
| - | |||
| - | + | === 1-0-2 7.2 PC PCI Express Software SDK === | |
| - | |||
| - | : | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The FPGA System CD contains a PC Windows based SDK to allow users to develop their 64-bit software application on 64-bits Windows XP/7/10. The SDK is located in the "CDROM\Demonstrations\PCIe_SW_KIT\Windows" folder which includes:</div>* PCI Express Driver |
| + | * PCI Express Library | ||
| + | * PCI Express Examples | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | : | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The kernel mode driver assumes the PCIe vendor ID (VID) is 0x1172 and the device ID (DID) is 0xE003. If different VID and DID are used in the design, users need to modify the PCIe vendor ID (VID) and device ID (DID) in the driver INF file accordingly.</div> |
| - | |||
| - | : | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The PCI Express Library is implemented as a single DLL named TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.DLL.This file is a 64-bit DLL. With the DLL is exported to the software API, users can easily communicate with the FPGA. The library provides the following functions:</div>* Basic data read and write |
| + | * Data read and write by DMA | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | : | + | <div style="color:#404040;">For high performance data transmission, Altera AVMM DMA is required as the read and write operations are specified under the hardware design on the FPGA.</div> |
| - | |||
| - | + | === 1-0-3 7.3 PCI Express Software Stack === | |
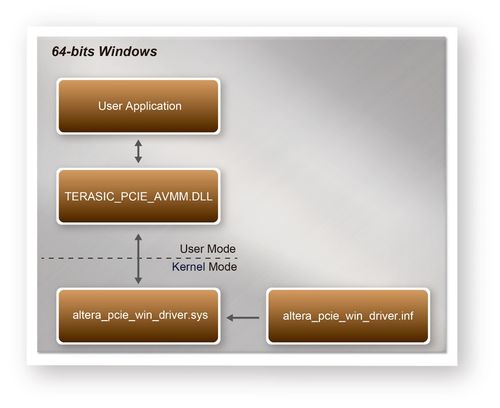
| + | [[#Figure72|Figure 7-2]]<span style="color:#1f4e79;"> '''</span>shows the software stack for the PCI Express application software on 64-bit Windows. The PCIe library module TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll provides DMA and direct I/O access for user application program to communicate with FPGA. Users can develop their applications based on this DLL. The altera_pcie_win_driver.sys kernel driver is provided by Altera. | ||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_2.jpg|500px]]</div> | |
| - | < | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-2 PCI Express Software Stack'''</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Install PCI Express Driver on Windows'''</div> |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | The | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The PCIe driver is locate in the folder:</div> |
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">"CDROM\Demonstrations\PCIe_SW_KIT\Windows\PCIe_Driver"</div> | |
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The folder includes the following four files:</div>* Altera_pcie_win_driver.cat | |
| + | * Altera_pcie_win_driver.inf | ||
| + | * Altera_pcie_win_driver.sys | ||
| + | * WdfCoinstaller01011.dll | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">To install the PCI Express driver, please execute the steps below: </div># Make sure the DE10-Advanced and the PC are both powered off. | |
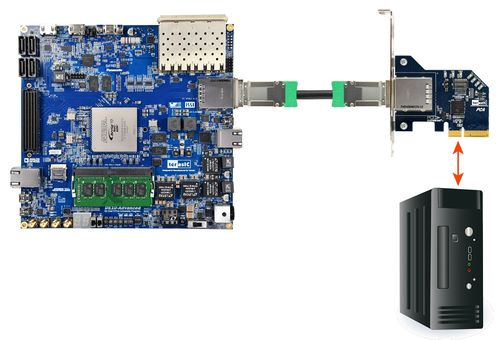
| + | # Plug the PCIe adapter card into the PCIe slot on the PC motherboard. Use the PCIe cable to connect to the DE10-Advanced PCIE connector and the PCIe adapter card (See<span style="color:#1f4e79;">''' </span>[[#Figure73|Figure 7-3]]) | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | = | + | <div style="margin-left:1.27cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_3.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-3 FPGA board connect to PC'''</div># Power on your DE10-Advanced board and the host PC | |
| + | # Make sure Altera Programmer and USB-Blaster II driver are installed | ||
| + | # Execute test.bat in "CDROM\Demonstrations\PCIe_Fundamental\demo_batch" to configure the FPGA | ||
| + | # Restart windows operation system | ||
| + | # Click Control Panel menu from Windows Start menu. Click Hardware and Sound item before clicking the Device Manager to launch the Device Manager dialog. There will be a PCI Device item in the dialog, as shown in [[#Figure74|Figure 7-4]]. Move the mouse cursor to the PCI Device item and right click it to select the Update Driver Software... item. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:1.27cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_4.jpg|500px]]</div> | |
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-4 Screenshot of launching Update Driver Software… dialog'''</div># In the '''How do you want to search for driver software''' dialog, click '''Browse my computer for driver software''' item, as shown in [[#Figure75|Figure 7-5]]<span style="color:#1f4e79;">.'''</span> | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <div style="text-align:center; | + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:1.27cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_5.jpg|500px]]. Click the '''Next''' button. |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:1.27cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_6.jpg|500px]], click the '''Install''' button. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"> | + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:1.27cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_7.jpg|500px]]. Click the '''Close''' button. |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:1.27cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_8.jpg|500px]]. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
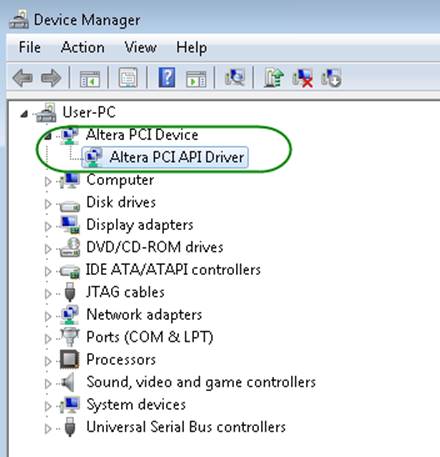
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:1.27cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_9.jpg|500px]]</div> | |
| - | <div style="text-align:center | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-9 Altera PCI API Driver in Device Manager'''</div> |
| - | |||
| - | + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Create a Software Application'''</div> | |
| - | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">All the files needed to create a PCIe software application are located in the directory CDROM\demonstration\PCIe_SW_KIT\Windows\PCIe_Library. It includes the following files:</div>* TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | ||
| + | * TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll (64-bit dll) | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">Below lists the procedures to use the SDK files in users’ C/C++ project :</div># Create a 64-bit C/C++ project. | |
| + | # Include TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h in the C/C++ project. | ||
| + | # Copy TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll to the folder where the project.exe is located. | ||
| + | # Dynamically load TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll in C/C++ program. To load the dll, please refer to the PCIe fundamental example below. | ||
| + | # Call the SDK API to implement the desired application. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">Users can easily communicate with the FPGA through the PCIe bus through the TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll API. The details of API are described below:</div> | ||
| - | + | === 1-0-4 7.4 PCI Express Library API === | |
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">Below shows the exported API in the TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll. The API prototype is defined in the TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h. </div> | |
| - | <div style=" | + | <div style="color:#404040;">Note: the Linux library terasic_pcie_qsys.so also use the same API and header file.</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''PCIE_Open'''</div> |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:15.251cm;" | |
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Function:''' | ||
| - | + | Open a specified PCIe card with vendor ID, device ID, and matched card index. | |
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Prototype:''' | ||
| - | + | PCIE_HANDLE PCIE_Open( | |
| - | + | uint8_t wVendorID, | |
| - | + | uint8_t wDeviceID, | |
| + | uint8_t wCardIndex); | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Parameters:''' | ||
| - | + | wVendorID: | |
| + | Specify the desired vendor ID. A zero value means to ignore the vendor ID. | ||
| - | + | wDeviceID: | |
| + | |||
| + | Specify the desired device ID. A zero value means to ignore the device ID. | ||
| + | |||
| + | wCardIndex: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the matched card index, a zero based index, based on the matched vendor ID and device ID. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Return Value:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Return a handle to presents specified PCIe card. A positive value is return if the PCIe card is opened successfully. A value zero means failed to connect the target PCIe card. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This handle value is used as a parameter for other functions, e.g. PCIE_Read32. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Users need to call PCIE_Close to release handle once the handle is no more used. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | | style="background-color:# | + | <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* '''PCIE_Close''' |
| - | | style="background-color:# | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:15.251cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Function:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Close a handle associated to the PCIe card. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Prototype:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | void PCIE_Close( | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE); | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Parameters:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | hPCIE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Return Value:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | None. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | | style=" | + | <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''PCIE_Read32'''</div> |
| - | | style="border:0.5pt solid # | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:15.251cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Function:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Read a 32-bit data from the FPGA board. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Prototype:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | bool PCIE_Read32( | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_BAR PcieBar, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_ADDRESS PcieAddress, | ||
| + | |||
| + | uint32_t *pdwData); | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Parameters:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | hPCIE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | PcieBar: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target BAR. | ||
| + | |||
| + | PcieAddress: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target address in FPGA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | pdwData: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A buffer to retrieve the 32-bit data. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Return Value:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Return '''true''' if read data is successful; otherwise '''false''' is returned. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | | style=" | + | <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''PCIE_Write32'''</div> |
| - | | style="border:0.5pt solid # | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:15.251cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Function:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Write a 32-bit data to the FPGA Board. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Prototype:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | bool PCIE_Write32( | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_BAR PcieBar, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_ADDRESS PcieAddress, | ||
| + | |||
| + | uint32_t dwData); | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Parameters:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | hPCIE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | PcieBar: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target BAR. | ||
| + | |||
| + | PcieAddress: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target address in FPGA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | dwData: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify a 32-bit data which will be written to FPGA board. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Return Value:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Return '''true''' if write data is successful; otherwise '''false''' is returned. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | | style=" | + | <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''PCIE_Read8'''</div> |
| - | | style="border:0.5pt solid # | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:15.251cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Function:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Read an 8-bit data from the FPGA board. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Prototype:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | bool PCIE_Read8( | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_BAR PcieBar, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_ADDRESS PcieAddress, | ||
| + | |||
| + | uint8_t *pByte); | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Parameters:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | hPCIE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | PcieBar: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target BAR. | ||
| + | |||
| + | PcieAddress: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target address in FPGA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | pByte: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A buffer to retrieve the 8-bit data. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Return Value:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Return '''true''' if read data is successful; otherwise '''false''' is returned. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | | style=" | + | <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''PCIE_Write8'''</div> |
| - | | style="border:0.5pt solid # | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:15.251cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Function:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Write an 8-bit data to the FPGA Board. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Prototype:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | bool PCIE_Write8( | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_BAR PcieBar, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_ADDRESS PcieAddress, | ||
| + | |||
| + | uint8_t Byte); | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Parameters:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | hPCIE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | PcieBar: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target BAR. | ||
| + | |||
| + | PcieAddress: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target address in FPGA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Byte: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify an 8-bit data which will be written to FPGA board. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Return Value:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Return '''true''' if write data is successful; otherwise '''false''' is returned. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | == | + | <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''PCIE_DmaRead'''</div> |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:15.251cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Function:''' | ||
| - | + | Read data from the memory-mapped memory of FPGA board in DMA. | |
| - | + | Maximal read size is (4GB-1) bytes. | |
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Prototype:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | bool PCIE_DmaRead( | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_LOCAL_ADDRESS LocalAddress, | ||
| + | |||
| + | void *pBuffer, | ||
| + | |||
| + | uint32_t dwBufSize | ||
| + | |||
| + | ); | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Parameters:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | hPCIE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | LocalAddress: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target memory-mapped address in FPGA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | pBuffer: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A pointer to a memory buffer to retrieved the data from FPGA. The size of buffer should be equal or larger the dwBufSize. | ||
| + | |||
| + | dwBufSize: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the byte number of data retrieved from FPGA. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Return Value:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Return '''true''' if read data is successful; otherwise '''false''' is returned. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | | style="background-color:# | + | <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''PCIE_DmaWrite'''</div> |
| - | + | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | | style=" | + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:15.251cm;" |
| - | | | + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" |
| + | || '''Function:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Write data to the memory-mapped memory of FPGA board in DMA. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Prototype:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | bool PCIE_DmaWrite( | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_LOCAL_ADDRESS LocalAddress, | ||
| + | |||
| + | void *pData, | ||
| + | |||
| + | uint32_t dwDataSize | ||
| + | |||
| + | ); | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Parameters:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | hPCIE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | LocalAddress: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target memory mapped address in FPGA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | pData: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A pointer to a memory buffer to store the data which will be written to FPGA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | dwDataSize: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the byte number of data which will be written to FPGA. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Return Value:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Return '''true''' if write data is successful; otherwise '''false''' is returned. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div> | ||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''PCIE_ConfigRead32'''</div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:15.251cm;" | |
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Function:''' | ||
| - | + | Read PCIe Configuration Table. Read a 32-bit data by given a byte offset. | |
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Prototype:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | bool PCIE_ConfigRead32 ( | ||
| + | |||
| + | PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, | ||
| + | |||
| + | uint32_t Offset, | ||
| + | |||
| + | uint32_t *pdwData | ||
| + | |||
| + | ); | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Parameters:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | hPCIE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Offset: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the target byte of offset in PCIe configuration table. | ||
| + | |||
| + | pdwData: | ||
| + | |||
| + | A 4-bytes buffer to retrieve the 32-bit data. | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#e6e6e6;border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding:0cm;" | ||
| + | || '''Return Value:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Return '''true''' if read data is successful; otherwise '''false''' is returned. | ||
| - | |||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | | style=" | + | |
| - | | style=" | + | === 1-0-5 7.5 PCIe Reference Design - Fundamental === |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | | style="border- | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The application reference design shows how to implement fundamental control and data transfer in DMA. In the design, basic I/O is used to control the BUTTON and LED on the FPGA board. High-speed data transfer is performed by DMA.</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Demonstration Files Location'''</div> |
| - | | style="border:0.5pt solid # | + | |
| - | | | + | |
| - | | style=" | + | |
| - | | style=" | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The demo file is located in the batch folder: </div> |
| - | | style="border:0.5pt solid # | + | |
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">CDROM\Demonstrations\ PCIe_Fundamental\demo_batch</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The folder includes following files:</div>* FPGA Configuration File: PCIe_Fundamental.sof | ||
| + | * Download Batch file: test.bat | ||
| + | * Windows Application Software folder : windows_app, includes | ||
| + | |||
| + | * PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL.exe | ||
| + | * TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.DLL | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="margin-left:1.693cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Demonstration Setup'''</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Install the FPGA board on your PC as shown in [[#Figure73|Figure 7-3]]. | ||
| + | # Configure FPGA with PCIe_Fundamental.sof by executing the test.bat. | ||
| + | # Install PCIe driver if necessary. The driver is located in the folder: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:0.635cm;margin-right:0cm;">CDROM\Demonstration\PCIe_SW_KIT\Windows\PCIe_Driver.</div># Restart Windows | ||
| + | # Make sure the Windows has detected the FPGA Board by checking the Windows Control panel as shown in [[#Figure710|Figure 7-10]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_10.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-10 Screenshot for PCIe Driver'''</div># Goto windows_app folder, execute PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL.exe. A menu will appear as shown in [[#Figure711|Figure 7-11]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_11.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-11 Screenshot of Program Menu'''</div># Type 0 followed by a ENTER key to select Led Control item, then input 15 (hex 0x0f) will make all led on as shown in [[#Figure712|Figure 7-12]]. If input 0 (hex 0x00), all led will be turn off. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_12.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-12 Screenshot of LED Control'''</div># Type 1 followed by an ENTER key to select Button Status Read item. The button status will be report as shown in [[#Figure713|Figure 7-13]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_13.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Figure 7-13 Screenshot of Button Status Report'''</span></div># Type 2 followed by an ENTER key to select DMA Testing item. The DMA test result will be report as shown in [[#Figure714|Figure 7-14]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_14.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Figure 7-14 Screenshot of DMA Memory Test Result'''</span></div># Type 99 followed by an ENTER key to exit this test program | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Development Tools'''</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Quartus Prime 18.0 Standard Edition | ||
| + | * Visual C++ 2012 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Demonstration Source Code Location'''</span></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Quartus Project: Demonstrations\PCIe_Fundamental | ||
| + | * C++ Project: Demonstrations\PCIe_SW_KIT\Windows\PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''FPGA Application Design'''</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
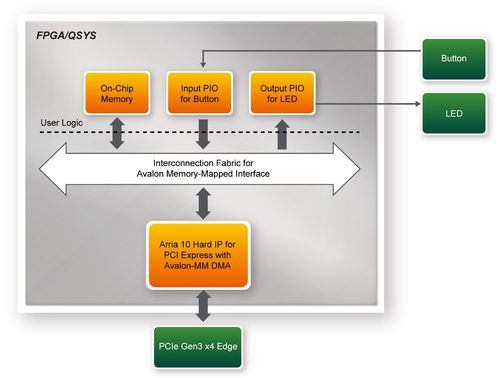
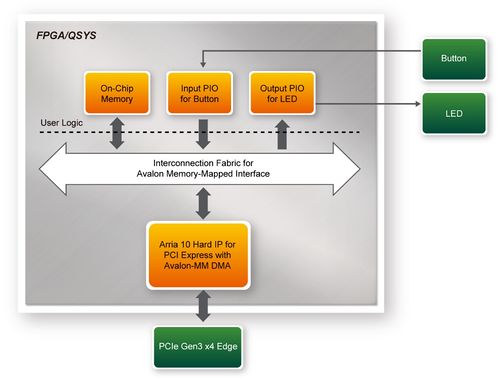
| + | [[#Figure715|Figure 7-15]] shows the system block diagram in the FPGA system. In the Qsys, Altera PIO controller is used to control the LED and monitor the Button Status, and the On-Chip memory is used for performing DMA testing. The PIO controllers and the On-Chip memory are connected to the PCI Express Hard IP controller through the Memory-Mapped Interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_15.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-15 Hardware block diagram of the PCIe reference design'''</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Windows Based Application Software Design'''</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The application software project is built by Visual C++ 2012. The project includes the following major files:</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:14.633cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#666633;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| <span style="color:#ffffff;">'''Name'''</span> | ||
| + | | align=center| <span style="color:#ffffff;">'''Description'''</span> | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL.cpp | ||
| + | || Main program | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE.c | ||
| + | || Implement dynamically load for TERAISC_PCIE_AVMM.DLL | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE.h | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | ||
| + | || SDK library file, defines constant and data structure | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |} |
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The main program PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL.cpp includes the header file "PCIE.h" and defines the controller address according to the FPGA design.</div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | <div style=" | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_16.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | + | ||
| - | <div style="color:# | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The base address of BUTTON and LED controllers are 0x4000010 and 0x4000020 based on PCIE_BAR4, in respectively. The on-chip memory base address is 0x00000000 relative to the DMA controller. </div> |
| - | <div style="color:# | + | |
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">Before accessing the FPGA through PCI Express, the application first calls PCIE_Load to dynamically load the TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll. Then, it call PCIE_Open to open the PCI Express driver. The constant DEFAULT_PCIE_VID and DEFAULT_PCIE_DID used in PCIE_Open are defined in TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h. If developer change the Vendor ID and Device ID and PCI Express IP, they also need to change the ID value define in TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h. If the return value of PCIE_Open is zero, it means the driver cannot be accessed successfully. In this case, please make sure:</div>* The FPGA is configured with the associated bit-stream file and the host is rebooted. | ||
| + | * The PCI express driver is loaded successfully. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The LED control is implemented by calling PCIE_Write32 API, as shown below:</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:15.333cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | || [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_17.jpg|500px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |} |
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The button status query is implemented by calling the PCIE_Read32 API, as shown below:</div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:15.134cm;" | |
| - | + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | |
| - | + | || [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_18.jpg|500px]] | |
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | < | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The memory-mapped memory read and write test is implemented by '''PCIE_DmaWrite''' and '''PCIE_DmaRead''' API, as shown below:</div> |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | === 1-0-6 7.6 PCIe Reference Design - DDR4 === | |
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The application reference design shows how to add DDR4 Memory Controllers for DDR4-A SODIMM and on board DDR4-B into the PCIe Quartus project based on the PCIe_Fundamental Quartus project and perform 4GB data DMA for both SODIMM. Also, this demo shows how to call “PCIE_ConfigRead32” API to check PCIe link status.</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Demonstration Files Location'''</div> | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The demo file is located in the batch folder: </div> | |
| - | <div style="text-align:center | + | <div style="text-align:center;">CDROM\Demonstrations\PCIe_DDR4\demo_batch</div> |
| - | <div style=" | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The folder includes following files:</div>* FPGA Configuration File: PCIe_DDR4.sof |
| + | * Download Batch file: test.bat | ||
| + | * Windows Application Software folder : windows_app, includes | ||
| + | * PCIE_DDR4.exe | ||
| + | * TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <div style=" | + | <div style="margin-left:0.847cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Demonstration Setup'''</div> |
| - | + | # Install DDR4 2400 4GB SODIMM on the FPGA board. | |
| + | # Install the FPGA board on your PC as shown in [[#Figure73|Figure 7-3]]. | ||
| + | # Configure FPGA with PCIe_DDR4.sof by executing the test.bat. | ||
| + | # Install PCIe driver if necessary. | ||
| + | # Restart Windows | ||
| + | # Make sure the Windows has detected the FPGA Board by checking the Windows Control panel. | ||
| + | # Goto windows_app folder, execute PCIE_DDR4.exe. A menu will appear as shown in [[#Figure716|Figure 7-16]]. | ||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_19.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-16 Screenshot of Program Menu'''</div># Type 2 followed by a ENTER key to select Link Info item. The PCIe link information will be shown as in [[#Figure717|Figure 7-17]]. Gen3 link speed and x8 link width are expected. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <div style="text-align:center | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_20.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"> | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-17 Screenshot of Link Info'''</div># Type 3 followed by an ENTER key to select DMA On-Chip Memory Test item. The DMA write and read test result will be report as shown in [[#Figure718|Figure 7-18]]. |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"> | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_21.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-18 Screenshot of On-Chip Memory DMA Test Result'''</div># Type 4 followed by an ENTER key to select DMA DDR4-A SODIMM Memory Test item. The DMA write and read test result will be report as shown in [[#Figure719|Figure 7-19]]. | |
| - | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_22.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-19 Screenshot of DDR4-A SOSIMM Memory DAM Test Result'''</div># Type 5 followed by an ENTER key to select DMA DDR4-B Memory Test item. The DMA write and read test result will be report as shown in [[#Figure720|Figure 7-20]]. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"> | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_23.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"> | + | <div style="text-align:center;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Figure 7-20 Screenshot of DDR4-B SOSIMM Memory DAM Test Result'''</span></div># Type 99 followed by an ENTER key to exit this test program. |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="margin-left:0.635cm;margin-right:0cm;"></div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Development Tools'''</div> | ||
| + | * Quartus Prime 18.0 Standard Edition | ||
| + | * Visual C++ 2012 | ||
| - | + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Demonstration Source Code Location'''</span></div> | |
| - | + | * Quartus Project: Demonstrations\PCIE_DDR4 | |
| + | * Visual C++ Project: Demonstrations\PCIe_SW_KIT\Windows\PCIe_DDR4 | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <div style=" | + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''FPGA Application Design'''</div> |
| - | |||
| - | |||
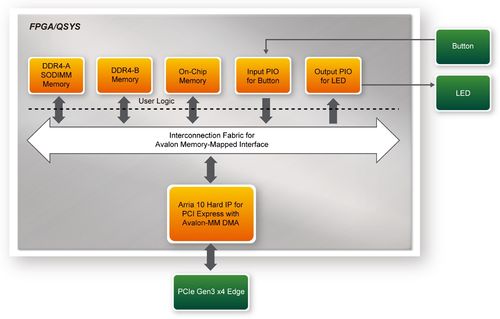
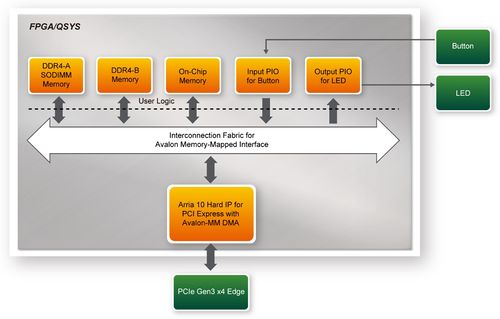
| - | + | [[#Figure721|Figure 7-21]] shows the system block diagram in the FPGA system. In the Qsys, Altera PIO controller is used to control the LED and monitor the Button Status, and the On-Chip memory is used for performing DMA testing. The PIO controllers and the On-Chip memory are connected to the PCI Express Hard IP controller through the Memory-Mapped Interface. | |
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"> | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_24.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 7-21 Hardware block diagram of the PCIe_DDR4 reference designWindows Based Application Software Design'''</div> | |
| - | <div style=" | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The application software project is built by Visual C++ 2012. The project includes the following major files:</div> |
| - | |||
| - | + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:14.633cm;" | |
| + | |- style="background-color:#666633;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| <span style="color:#ffffff;">'''Name'''</span> | ||
| + | | align=center| <span style="color:#ffffff;">'''Description'''</span> | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE_DDR4.cpp | ||
| + | || Main program | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE.c | ||
| + | || Implement dynamically load for TERAISC_PCIE_AVMM.DLL | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE.h | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | ||
| + | || SDK library file, defines constant and data structure | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The main program PCIE_DDR4.cpp includes the header file "PCIE.h" and defines the controller address according to the FPGA design.</div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"> | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_25.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The base address of BUTTON and LED controllers are 0x4000010 and 0x4000020 based on PCIE_BAR4, in respectively. The on-chip memory base address is 0x00000000 relative to the DMA controller. <span style="color:#ff0000;">The above definition is the same as those in PCIe Fundamental demo.</span></div> | |
| - | |||
| - | <div style=" | + | <div style="color:#404040;">Before accessing the FPGA through PCI Express, the application first calls PCIE_Load to dynamically load the TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.DLL. Then, it call PCIE_Open to open the PCI Express driver. The constant DEFAULT_PCIE_VID and DEFAULT_PCIE_DID used in PCIE_Open are defined in TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h. If developer change the Vendor ID and Device ID and PCI Express IP, they also need to change the ID value define in TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h. If the return value of PCIE_Open is zero, it means the driver cannot be accessed successfully. In this case, please make sure:</div>* The FPGA is configured with the associated bit-stream file and the host is rebooted. |
| + | * The PCI express driver is loaded successfully. | ||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The LED control is implemented by calling PCIE_Write32 API, as shown below:</div> | |
| - | |||
| - | + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:15.039cm;" | |
| - | + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | |
| - | + | || [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_26.jpg|500px]] | |
| - | + | |- | |
| - | + | |} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The button status query is implemented by calling the '''PCIE_Read32''' API, as shown below:</div> | |
| + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:15.134cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | || [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_27.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;"></div> | ||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The memory-mapped memory read and write test is implemented by '''PCIE_DmaWrite''' and '''PCIE_DmaRead''' API, as shown below:</div> | |
| - | + | [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_28.jpg|500px]] | |
| - | |||
| + | The PCIe link information is implemented by PCIE_ConfigRead32 API, as shown below: | ||
| - | + | = | |
| + | = <span style="color:#000000;">Chapter 8</span><span style="color:#000080;"><span style="color:#002060;">Chpater2 PCI Express Reference Design for Linux</span></span> == | ||
| - | |||
| - | <div style=" | + | <div style="color:#404040;">PCI Express is commonly used in consumer, server, and industrial applications, to link motherboard-mounted peripherals. From this demonstration, it will show how the PC Linux and FPGA communicate with each other through the PCI Express interface. Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express with Avalon-MM DMA IP is used in this demonstration. For detail about this IP, please refer to Altera document [https://www.altera.com/en_US/pdfs/literature/ug/ug_a10_pcie_avmm_dma.pdf ug_a10_pcie_avmm_dma.pdf].</div> |
| - | |||
| - | + | === 2-0-7 8.1 PCI Express System Infrastructure === | |
| - | |||
| - | + | [[#Figure81|Figure 8-1]] shows the infrastructure of the PCI Express System in this demonstration. It consists of two primary components: FPGA System and PC System. The FPGA System is developed based on Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express with Avalon-MM DMA. The application software on the PC side is developed by Terasic based on Altera’s PCIe kernel mode driver. | |
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_29.jpg|500px]]</div> | |
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"> | + | <div style="text-align:center;"> '''Figure 8-1 Infrastructure of PCI Express System'''</div> |
| - | |||
| + | === 2-0-8 8.2 PC PCI Express Software SDK === | ||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The FPGA System CD contains a PC Windows based SDK to allow users to develop their 64-bit software application on 64-bits Linux. CentOS 7.2 is recommended. The SDK is located in the “CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_SW_KIT/Linux” folder which includes:</div>* PCI Express Driver | |
| + | * PCI Express Library | ||
| + | * PCI Express Examples | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | = | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The kernel mode driver assumes the PCIe vendor ID (VID) is 0x1172 and the device ID (DID) is 0xE003. If different VID and DID are used in the design, users need to modify the PCIe vendor ID (VID) and device ID (DID) in the driver project and rebuild the driver. The ID is defined in the file PCIe_SW_KIT/Linux/PCIe_Driver/altera_pcie_cmd.h.</div> |
| - | |||
| - | <div style=" | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The PCI Express Library is implemented as a single .so file named terasic_pcie_qsys.so.This file is a 64-bit library file. With the library exported software API, users can easily communicate with the FPGA. The library provides the following functions:</div>* Basic data read and write |
| + | * Data read and write by DMA | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">For high performance data transmission, Altera AVMM DMA is required as the read and write operations are specified under the hardware design on the FPGA.</div> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | === 2-0-9 8.3 PCI Express Software Stack === | |
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | ||
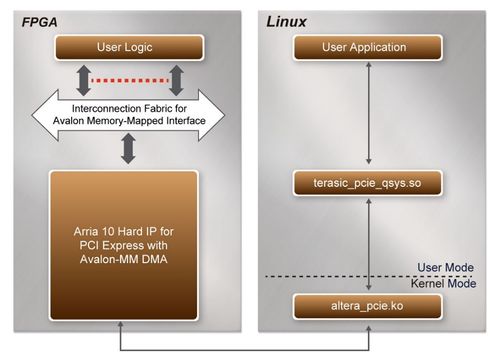
| - | + | [[#Figure82|Figure 8-2]] shows the software stack for the PCI Express application software on 64-bit Linux. The PCIe library module terasic_pcie_qys.so provides DMA and direct I/O access for user application program to communicate with FPGA. Users can develop their applications based on this .so library file. The altera_pcie.ko kernel driver is provided by Altera. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_30.jpg|500px]]</div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;"> '''Figure 8-2 PCI Express Software Stack'''</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Install PCI Express Driver on Linux'''</div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
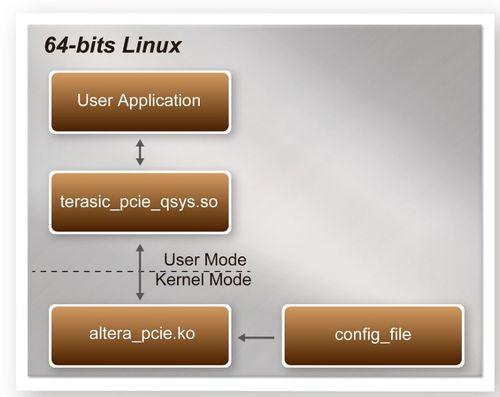
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">To make sure the PCIe driver can meet your kernel of Linux distribution, the driver altera_pcie.ko should be recompile before use it. The PCIe driver project is locate in the folder:</div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">"CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_SW_KIT/Linux/PCIe_Driver"</div> | |
| - | | style="border | + | |
| - | |- | + | The folder includes the following files:* altera_pcie.c |
| - | + | * altera_pcie.h | |
| - | | | + | * altera_pcie_cmd.h |
| + | * <div style="margin-left:1.7cm;margin-right:0cm;">Makefile</div> | ||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:1.7cm;margin-right:0cm;">load_driver</div> | ||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:1.7cm;margin-right:0cm;">unload</div> | ||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:1.7cm;margin-right:0cm;">config_file</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">To compile and install the PCI Express driver, please execute the steps below: </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | # Make sure the DE10-Advanced and the PC are both powered off. | ||
| + | # Plug the PCIe adapter card into the PCIe slot on the PC motherboard. Use the PCIe cable to connect to the DE10-Advanced PCIE connector and the PCIe adapter card (See [[#Figure83|Figure 8-3]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:1.27cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_31.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-3 FPGA board connect to PC'''</div># Power on your DE10-Advanced board and the host PC | ||
| + | # Open a terminal and use "cd" command to goto the folder"CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_Fundamental/demo_batch". | ||
| + | # Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable pointing to the Quartus installation path. Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable by tying the following commands in terminal. Replace “/home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus” to your quartus installation path. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:13.938cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | || export QUARTUS_ROOTDIR=/home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | # Execute "sudo -E sh test.sh" command to configure the FPGA | |
| + | # Restart Linux operation system. In Linux, open a terminal and use “cd” command to goto the PCIe_Driver folder | ||
| + | # Type the following commands to compile and install the driver altera_pcie.ko, and make sure driver is loaded successfully and FPGA is detected by the driver as shown in [[#Figure84|Figure 8-4]].''' | ||
| - | + | * make | |
| + | * sudo sh load_driver | ||
| + | * dmesg | tail -n 15 | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_32.jpg|500px]] | |
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-4 Screenshot of install PCIe driver'''</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Create a Software Application'''</div> | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">All the files needed to create a PCIe software application are located in the directory CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_SW_KIT/Linux/PCIe_Library. It includes the following files:</div>* TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | |
| + | * terasic_pcie_qsys.so (64-bit library) | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">Below lists the procedures to use the library in users’ C/C++ project:</div># Create a 64-bit C/C++ project. | ||
| + | # Include TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h in the C/C++ project. | ||
| + | # Copy terasic_pcie_qsys.so to the folder where the project execution file is located. | ||
| + | # Dynamically load terasic_pcie_qsys.so in C/C++ program. To load the terasic_pcie_qsys.so, please refer to the PCIe fundamental example below. | ||
| + | # Call the library API to implement the desired application. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">Users can easily communicate with the FPGA through the PCIe bus through the terasic_pcie_qsys.so API. The details of API are described below:</div> | |
| + | === 2-0-10 8.4 PCI Express Library API === | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The API is the same as Windows Library. Please refer to the section 7.4 PCI Express Library API in this document.</div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | === 2-0-11 8.5 PCIe Reference Design – Fundamental === | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The application reference design shows how to implement fundamental control and data transfer in DMA. In the design, basic I/O is used to control the BUTTON and LED on the FPGA board. High-speed data transfer is performed by DMA.</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Demonstration Files Location'''</div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The demo file is located in the batch folder: </div> | ||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_Fundamental/demo_batch</div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <div style=" | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The folder includes following files:</div>* FPGA Configuration File: PCIe_Fundamental.sof |
| - | + | * Download Batch file: test.sh | |
| - | * | + | * Linux Application Software folder : linux_app, includes |
| - | * | + | |
| + | * PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL | ||
| + | * terasic_pcie_qsys.so | ||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Demonstration Setup'''</div> | ||
| - | + | # Install the FPGA board on your PC as shown in [[#Figure83|Figure8-3]]. | |
| + | # Open a terminal and use "cd" command to goto "CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_Fundamental/demo_batch". | ||
| + | # Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable pointing to the Quartus installation path. Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable by tying the following commands in terminal. Replace /home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus to your quartus installation path. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:13.938cm;" | |
| + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | || export QUARTUS_ROOTDIR=/home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | # Execute "sudo -E sh test.sh" command to configure the FPGA | ||
| + | # Restart Linux | ||
| + | # Install PCIe driver. The driver is located in the folder: | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:0.635cm;margin-right:0cm;">CDROM/Demonstration/PCIe_SW_KIT/Linux/PCIe_Driver.</div># Type “ls –l /dev/altera_pcie*” to make sure the Linux has detected the FPGA Board. If the FPGA board is detected, developers can find the /dev/altera_pcieX(where X is 0~255) in Linux file system as shown below. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_33.jpg|500px]]. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_34.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-5 Screenshot of Program Menu'''</div># Type 0 followed by a ENTER key to select Led Control item, then input 3 (hex 0x03) will make all led on as shown in [[#Figure86|Figure 8-6]]. If input 0 (hex 0x00), all led will be turn off. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_35.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-6 Screenshot of LED Control'''</div># <div style="margin-left:0.63cm;margin-right:0cm;">Type 1 followed by an ENTER key to select Button Status Read item. The button status will be report as shown in [[#Figure87|Figure 8-7]].</div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:-0.005cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_36.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-7 Screenshot of Button Status Report'''</div># <div style="margin-left:0.63cm;margin-right:0cm;">Type 2 followed by an ENTER key to select DMA Testing item. The DMA test result will be report as shown in [[#Figure88|Figure 8-8]].</div> | ||
| - | <div style="text-align:center; | + | <div style="text-align:center;margin-left:-0.005cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_37.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"> | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-8 Screenshot of DMA Memory Test Result'''</div># Type 99 followed by an ENTER key to exit this test program |
| - | + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Development Tools'''</div> | |
| + | * Quartus Prime 18.0 Standard Edition | ||
| + | * GNU Compiler Collection, Version 4.8 is recommend | ||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Demonstration Source Code Location'''</span></div> | ||
| - | + | * Quartus Project: Demonstrations/PCIe_Fundamental | |
| + | * C++ Project: Demonstrations/PCIe_SW_KIT/Linux/PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL | ||
| - | + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''FPGA Application Design'''</div> | |
| - | + | ||
| + | [[#Figure89|Figure 8-9]] shows the system block diagram in the FPGA system. In the Qsys, Altera PIO controller is used to control the LED and monitor the Button Status, and the On-Chip memory is used for performing DMA testing. The PIO controllers and the On-Chip memory are connected to the PCI Express Hard IP controller through the Memory-Mapped Interface. | ||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_38.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-9 Hardware block diagram of the PCIe reference design'''</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Linux Based Application Software Design'''The application software project is built by GNU Toolchain. The project includes the following major files:</div> | |
| - | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width: | + | |
| + | |||
| + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:14.633cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#666633;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| <span style="color:#ffffff;">'''Name'''</span> | ||
| + | | align=center| <span style="color:#ffffff;">'''Description'''</span> | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL.cpp | ||
| + | || Main program | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE.c | ||
| + | || Implement dynamically load for terasic_pcie_qsys.so library file | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE.h | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | ||
| + | || SDK library file, defines constant and data structure | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | | style="border- | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The main program PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL.cpp includes the header file "PCIE.h" and defines the controller address according to the FPGA design.</div> |
| - | + | ||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_39.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The base address of BUTTON and LED controllers are 0x4000010 and 0x4000020 based on PCIE_BAR4, in respectively. The on-chip memory base address is 0x00000000 relative to the DMA controller. </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">Before accessing the FPGA through PCI Express, the application first calls PCIE_Load to dynamically load the terasic_pcie_qsys.so. Then, it call PCIE_Open to open the PCI Express driver. The constant DEFAULT_PCIE_VID and DEFAULT_PCIE_DID used in PCIE_Open are defined in TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h. If developer change the Vendor ID and Device ID and PCI Express IP, they also need to change the ID value define in TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h. If the return value of PCIE_Open is zero, it means the driver cannot be accessed successfully. In this case, please make sure:</div>* The FPGA is configured with the associated bit-stream file and the host is rebooted. | ||
| + | * The PCI express driver is loaded successfully. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The LED control is implemented by calling PCIE_Write32 API, as shown below:</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:15.333cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | || [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_40.jpg|500px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | | style="border- | + | <div style="color:#404040;"></div> |
| - | + | ||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The button status query is implemented by calling the '''PCIE_Read32''' API, as shown below:</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:15.134cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | || [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_41.jpg|500px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | style=" | + | |} |
| - | + | <div style="color:#404040;">The memory-mapped memory read and write test is implemented by '''PCIE_DmaWrite''' and '''PCIE_DmaRead''' API, as shown below:</div> | |
| - | | style="border:0.5pt solid # | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === 2-0-12 8.5 PCIe Reference Design - DDR4 === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The application reference design shows how to add DDR4 Memory Controllers for DDR4-A SODIMM and on board DDR4-B into the PCIe Quartus project based on the PCIe_Fundamental Quartus project and perform 4GB data DMA for both SODIMM. Also, this demo shows how to call “PCIE_ConfigRead32” API to check PCIe link status.</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Demonstration Files Location'''</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The demo file is located in the batch folder: </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">CDROM/Demonstrations/ PCIe_DDR4/demo_batch</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The folder includes following files:</div>* FPGA Configuration File: PCIe_DDR4sof | ||
| + | * Download Batch file: test.sh | ||
| + | * Linux Application Software folder : linux_app, includes | ||
| + | |||
| + | * PCIE_DDR4 | ||
| + | * terasic_pcie_qsys.so | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Demonstration Setup'''</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Install DDR4 2400 4GB SODIMM on the FPGA board. | ||
| + | # Install the FPGA board on your PC as shown in [[#Figure83|Figure8-3]]. | ||
| + | # Open a terminal and use "cd" command to goto "CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_Fundamental/demo_batch". | ||
| + | # Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable pointing to the Quartus installation path. Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable by tying the following commands in terminal. Replace /home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus to your quartus installation path. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="border-spacing:0;width:13.938cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | || export QUARTUS_ROOTDIR=/home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |} |
| - | | style=" | + | # Execute "sudo -E sh test.sh" command to configure the FPGA |
| - | + | # Restart Linux | |
| - | + | # Install PCIe driver. | |
| - | + | # Make sure the Linux has detected the FPGA Board. | |
| - | + | # Goto linux_app folder, execute PCIE_DDR4. A menu will appear as shown in [[#Figure810|Figure 8-10]]. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_42.jpg|500px]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-10 Screenshot of Program Menu'''</div># Type 2 followed by an ENTER key to select Link Info item. The PCIe link information will be shown as in [[#Figure811|Figure 8-11]]. Gen3 link speed and x8 link width are expected. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_43.jpg|500px]] | |
| - | | style="border- | + | |
| - | + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-11 Screenshot of Link Info'''</div># <div style="margin-left:0.63cm;margin-right:0cm;">Type 3 followed by an ENTER key to select DMA On-Chip Memory Test item. The DMA write and read test result will be report as shown in [[#Figure812|Figure 8-12]].</div> | |
| - | | style=" | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | | style=" | + | <div style="margin-left:-0.005cm;margin-right:0cm;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_44.jpg|500px]]</div> |
| - | + | ||
| - | | | + | <div style="text-align:center;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Figure 8-12 Screenshot of On-Chip Memory DMA Test Result'''</span></div># Type 4 followed by an ENTER key to select DMA DDR4-A SODIMM Memory Test item. The DMA write and read test result will be report as shown in [[#Figure814|Figure 8-14]]. |
| - | | style=" | + | |
| - | | style=" | + | |
| - | | | + | |
| + | [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_45.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Figure 8-14 Screenshot of DDR4-A SOSIMM Memory DAM Test Result'''</span></div># Type 5 followed by an ENTER key to select DMA DDR4-B Memory Test item. The DMA write and read test result will be report as shown in [[#Figure815|Figure 8-15]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_46.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Figure 8-15 Screenshot of DDR4-B SOSIMM Memory DAM Test Result'''</span></div># Type 99 followed by an ENTER key to exit this test program. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Development Tools'''</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Quartus Prime 18.0 Standard Edition | ||
| + | * GNU Compiler Collection, Version 4.8 is recommended | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;"><span style="color:#404040;">'''Demonstration Source Code Location'''</span></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Quartus Project: Demonstrations/PCIE_DDR4 | ||
| + | * C++ Project: Demonstrations/PCIe_SW_KIT/Linux/PCIe_DDR4 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''FPGA Application Design'''</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">[[#Figure816|Figure 8-16]] shows the system block diagram in the FPGA system. In the Qsys, Altera PIO controller is used to control the LED and monitor the Button Status, and the On-Chip memory is used for performing DMA testing. The PIO controllers and the On-Chip memory are connected to the PCI Express Hard IP controller through the Memory-Mapped Interface.</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_47.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">'''Figure 8-16 Hardware block diagram of the PCIe_DDR4 reference design'''</div>* <div style="margin-left:0cm;margin-right:0cm;">'''Linux Based Application Software Design'''</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The application software project is built by GNU Toolchain. The project includes the following major files:</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:14.633cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#666633;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| <span style="color:#ffffff;">'''Name'''</span> | ||
| + | | align=center| <span style="color:#ffffff;">'''Description'''</span> | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE_DDR4.cpp | ||
| + | || Main program | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE.c | ||
| + | || Implement dynamically load for terasic_pcie_qsys.so library file | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| PCIE.h | ||
| + | |- style="background-color:#ffffcc;border:0.5pt solid #a6a6a6;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | | align=center| TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | ||
| + | || SDK library file, defines constant and data structure | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The main program PCIE_DDR4.cpp includes the header file "PCIE.h" and defines the controller address according to the FPGA design.</div> | ||
| + | <div style="text-align:center;">[[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_48.jpg|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The base address of BUTTON and LED controllers are 0x4000010 and 0x4000020 based on PCIE_BAR4, in respectively. The on-chip memory base address is 0x00000000 relative to the DMA controller. <span style="color:#ff0000;">The above definition is the same as those in PCIe Fundamental demo.</span></div> | ||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">Before accessing the FPGA through PCI Express, the application first calls PCIE_Load to dynamically load the terasic_pcie_qsys.so. Then, it call PCIE_Open to open the PCI Express driver. The constant DEFAULT_PCIE_VID and DEFAULT_PCIE_DID used in PCIE_Open are defined in TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h. If developer change the Vendor ID and Device ID and PCI Express IP, they also need to change the ID value define in TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h. If the return value of PCIE_Open is zero, it means the driver cannot be accessed successfully. In this case, please make sure:</div>* The FPGA is configured with the associated bit-stream file and the host is rebooted. | ||
| + | * The PCI express driver is loaded successfully. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The LED control is implemented by calling PCIE_Write32 API, as shown below:</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:15.039cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | || [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_49.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The button status query is implemented by calling the '''PCIE_Read32''' API, as shown below:</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| align="center" style="border-spacing:0;width:15.134cm;" | ||
| + | |- style="border:0.5pt solid #00000a;padding-top:0cm;padding-bottom:0cm;padding-left:0.191cm;padding-right:0.191cm;" | ||
| + | || [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_50.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <div style="color:#404040;">The memory-mapped memory read and write test is implemented by '''PCIE_DmaWrite''' and '''PCIE_DmaRead''' API, as shown below:</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image: DE10-Advanced_revC_PCIE_pic_51.jpg|500px]] | ||
| - | + | The PCIe link information is implemented by PCIE_ConfigRead32 API, as shown below: | |
Latest revision as of 13:31, 27 August 2018
=
Contents |
Chpater1 Chapter 7PCI Express Design for Windows =
1-0-1 7.1 PCI Express System Infrastructure
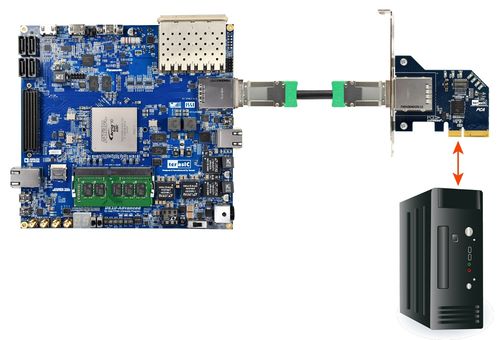
Figure 7-1 shows the infrastructure of the PCI Express System in this demonstration. It consists of two primary components: FPGA System and PC System. The FPGA System is developed based on Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express with Avalon-MM DMA. The application software on the PC side is developed by Terasic based on Altera’s PCIe kernel mode driver.
1-0-2 7.2 PC PCI Express Software SDK
- PCI Express Library
- PCI Express Examples
- Data read and write by DMA
1-0-3 7.3 PCI Express Software Stack
Figure 7-2 shows the software stack for the PCI Express application software on 64-bit Windows. The PCIe library module TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll provides DMA and direct I/O access for user application program to communicate with FPGA. Users can develop their applications based on this DLL. The altera_pcie_win_driver.sys kernel driver is provided by Altera.
- Altera_pcie_win_driver.inf
- Altera_pcie_win_driver.sys
- WdfCoinstaller01011.dll
- Plug the PCIe adapter card into the PCIe slot on the PC motherboard. Use the PCIe cable to connect to the DE10-Advanced PCIE connector and the PCIe adapter card (See Figure 7-3)
- Make sure Altera Programmer and USB-Blaster II driver are installed
- Execute test.bat in "CDROM\Demonstrations\PCIe_Fundamental\demo_batch" to configure the FPGA
- Restart windows operation system
- Click Control Panel menu from Windows Start menu. Click Hardware and Sound item before clicking the Device Manager to launch the Device Manager dialog. There will be a PCI Device item in the dialog, as shown in Figure 7-4. Move the mouse cursor to the PCI Device item and right click it to select the Update Driver Software... item.
- Create a Software Application
- TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll (64-bit dll)
- Include TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h in the C/C++ project.
- Copy TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll to the folder where the project.exe is located.
- Dynamically load TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll in C/C++ program. To load the dll, please refer to the PCIe fundamental example below.
- Call the SDK API to implement the desired application.
1-0-4 7.4 PCI Express Library API
| Function:
Open a specified PCIe card with vendor ID, device ID, and matched card index. |
| Prototype:
PCIE_HANDLE PCIE_Open( uint8_t wVendorID, uint8_t wDeviceID, uint8_t wCardIndex); |
| Parameters:
wVendorID: Specify the desired vendor ID. A zero value means to ignore the vendor ID. wDeviceID: Specify the desired device ID. A zero value means to ignore the device ID. wCardIndex: Specify the matched card index, a zero based index, based on the matched vendor ID and device ID. |
| Return Value:
Return a handle to presents specified PCIe card. A positive value is return if the PCIe card is opened successfully. A value zero means failed to connect the target PCIe card. This handle value is used as a parameter for other functions, e.g. PCIE_Read32. Users need to call PCIE_Close to release handle once the handle is no more used. |
| Function:
Close a handle associated to the PCIe card. |
| Prototype:
void PCIE_Close( PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE); |
| Parameters:
hPCIE: A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. |
| Return Value:
None. |
| Function:
Read a 32-bit data from the FPGA board. |
| Prototype:
bool PCIE_Read32( PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, PCIE_BAR PcieBar, PCIE_ADDRESS PcieAddress, uint32_t *pdwData); |
| Parameters:
hPCIE: A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. PcieBar: Specify the target BAR. PcieAddress: Specify the target address in FPGA. pdwData: A buffer to retrieve the 32-bit data. |
| Return Value:
Return true if read data is successful; otherwise false is returned. |
| Function:
Write a 32-bit data to the FPGA Board. |
| Prototype:
bool PCIE_Write32( PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, PCIE_BAR PcieBar, PCIE_ADDRESS PcieAddress, uint32_t dwData); |
| Parameters:
hPCIE: A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. PcieBar: Specify the target BAR. PcieAddress: Specify the target address in FPGA. dwData: Specify a 32-bit data which will be written to FPGA board. |
| Return Value:
Return true if write data is successful; otherwise false is returned. |
| Function:
Read an 8-bit data from the FPGA board. |
| Prototype:
bool PCIE_Read8( PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, PCIE_BAR PcieBar, PCIE_ADDRESS PcieAddress, uint8_t *pByte); |
| Parameters:
hPCIE: A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. PcieBar: Specify the target BAR. PcieAddress: Specify the target address in FPGA. pByte: A buffer to retrieve the 8-bit data. |
| Return Value:
Return true if read data is successful; otherwise false is returned. |
| Function:
Write an 8-bit data to the FPGA Board. |
| Prototype:
bool PCIE_Write8( PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, PCIE_BAR PcieBar, PCIE_ADDRESS PcieAddress, uint8_t Byte); |
| Parameters:
hPCIE: A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. PcieBar: Specify the target BAR. PcieAddress: Specify the target address in FPGA. Byte: Specify an 8-bit data which will be written to FPGA board. |
| Return Value:
Return true if write data is successful; otherwise false is returned. |
| Function:
Read data from the memory-mapped memory of FPGA board in DMA. Maximal read size is (4GB-1) bytes. |
| Prototype:
bool PCIE_DmaRead( PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, PCIE_LOCAL_ADDRESS LocalAddress, void *pBuffer, uint32_t dwBufSize ); |
| Parameters:
hPCIE: A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. LocalAddress: Specify the target memory-mapped address in FPGA. pBuffer: A pointer to a memory buffer to retrieved the data from FPGA. The size of buffer should be equal or larger the dwBufSize. dwBufSize: Specify the byte number of data retrieved from FPGA. |
| Return Value:
Return true if read data is successful; otherwise false is returned. |
| Function:
Write data to the memory-mapped memory of FPGA board in DMA. |
| Prototype:
bool PCIE_DmaWrite( PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, PCIE_LOCAL_ADDRESS LocalAddress, void *pData, uint32_t dwDataSize ); |
| Parameters:
hPCIE: A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. LocalAddress: Specify the target memory mapped address in FPGA. pData: A pointer to a memory buffer to store the data which will be written to FPGA. dwDataSize: Specify the byte number of data which will be written to FPGA. |
| Return Value:
Return true if write data is successful; otherwise false is returned. |
- PCIE_ConfigRead32
| Function:
Read PCIe Configuration Table. Read a 32-bit data by given a byte offset. |
| Prototype:
bool PCIE_ConfigRead32 ( PCIE_HANDLE hPCIE, uint32_t Offset, uint32_t *pdwData ); |
| Parameters:
hPCIE: A PCIe handle return by PCIE_Open function. Offset: Specify the target byte of offset in PCIe configuration table. pdwData: A 4-bytes buffer to retrieve the 32-bit data. |
| Return Value:
Return true if read data is successful; otherwise false is returned.
|
1-0-5 7.5 PCIe Reference Design - Fundamental
- Download Batch file: test.bat
- Windows Application Software folder : windows_app, includes
- PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL.exe
- TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.DLL
- Install the FPGA board on your PC as shown in Figure 7-3.
- Configure FPGA with PCIe_Fundamental.sof by executing the test.bat.
- Install PCIe driver if necessary. The driver is located in the folder:
- Make sure the Windows has detected the FPGA Board by checking the Windows Control panel as shown in Figure 7-10.
- Development Tools
- Quartus Prime 18.0 Standard Edition
- Visual C++ 2012
- Demonstration Source Code Location
- Quartus Project: Demonstrations\PCIe_Fundamental
- C++ Project: Demonstrations\PCIe_SW_KIT\Windows\PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL
- FPGA Application Design
Figure 7-15 shows the system block diagram in the FPGA system. In the Qsys, Altera PIO controller is used to control the LED and monitor the Button Status, and the On-Chip memory is used for performing DMA testing. The PIO controllers and the On-Chip memory are connected to the PCI Express Hard IP controller through the Memory-Mapped Interface.
| Name | Description |
| PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL.cpp | Main program |
| PCIE.c | Implement dynamically load for TERAISC_PCIE_AVMM.DLL |
| PCIE.h | |
| TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | SDK library file, defines constant and data structure |
- The PCI express driver is loaded successfully.
| 500px |
| 500px |
1-0-6 7.6 PCIe Reference Design - DDR4
- Download Batch file: test.bat
- Windows Application Software folder : windows_app, includes
- PCIE_DDR4.exe
- TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.dll
- Install DDR4 2400 4GB SODIMM on the FPGA board.
- Install the FPGA board on your PC as shown in Figure 7-3.
- Configure FPGA with PCIe_DDR4.sof by executing the test.bat.
- Install PCIe driver if necessary.
- Restart Windows
- Make sure the Windows has detected the FPGA Board by checking the Windows Control panel.
- Goto windows_app folder, execute PCIE_DDR4.exe. A menu will appear as shown in Figure 7-16.
- Quartus Prime 18.0 Standard Edition
- Visual C++ 2012
- Demonstration Source Code Location
- Quartus Project: Demonstrations\PCIE_DDR4
- Visual C++ Project: Demonstrations\PCIe_SW_KIT\Windows\PCIe_DDR4
- FPGA Application Design
Figure 7-21 shows the system block diagram in the FPGA system. In the Qsys, Altera PIO controller is used to control the LED and monitor the Button Status, and the On-Chip memory is used for performing DMA testing. The PIO controllers and the On-Chip memory are connected to the PCI Express Hard IP controller through the Memory-Mapped Interface.
| Name | Description |
| PCIE_DDR4.cpp | Main program |
| PCIE.c | Implement dynamically load for TERAISC_PCIE_AVMM.DLL |
| PCIE.h | |
| TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | SDK library file, defines constant and data structure |
- The PCI express driver is loaded successfully.
| 500px |
| 500px |
The PCIe link information is implemented by PCIE_ConfigRead32 API, as shown below:
=
Chapter 8Chpater2 PCI Express Reference Design for Linux =
2-0-7 8.1 PCI Express System Infrastructure
Figure 8-1 shows the infrastructure of the PCI Express System in this demonstration. It consists of two primary components: FPGA System and PC System. The FPGA System is developed based on Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express with Avalon-MM DMA. The application software on the PC side is developed by Terasic based on Altera’s PCIe kernel mode driver.
2-0-8 8.2 PC PCI Express Software SDK
- PCI Express Library
- PCI Express Examples
- Data read and write by DMA
2-0-9 8.3 PCI Express Software Stack
Figure 8-2 shows the software stack for the PCI Express application software on 64-bit Linux. The PCIe library module terasic_pcie_qys.so provides DMA and direct I/O access for user application program to communicate with FPGA. Users can develop their applications based on this .so library file. The altera_pcie.ko kernel driver is provided by Altera.
The folder includes the following files:* altera_pcie.c
- altera_pcie.h
- altera_pcie_cmd.h
- Makefile
- load_driver
- unload
- config_file
- Make sure the DE10-Advanced and the PC are both powered off.
- Plug the PCIe adapter card into the PCIe slot on the PC motherboard. Use the PCIe cable to connect to the DE10-Advanced PCIE connector and the PCIe adapter card (See Figure 8-3)
- Open a terminal and use "cd" command to goto the folder"CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_Fundamental/demo_batch".
- Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable pointing to the Quartus installation path. Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable by tying the following commands in terminal. Replace “/home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus” to your quartus installation path.
| export QUARTUS_ROOTDIR=/home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus |
- Execute "sudo -E sh test.sh" command to configure the FPGA
- Restart Linux operation system. In Linux, open a terminal and use “cd” command to goto the PCIe_Driver folder
- Type the following commands to compile and install the driver altera_pcie.ko, and make sure driver is loaded successfully and FPGA is detected by the driver as shown in Figure 8-4.
- make
- sudo sh load_driver
- dmesg | tail -n 15
- terasic_pcie_qsys.so (64-bit library)
- Include TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h in the C/C++ project.
- Copy terasic_pcie_qsys.so to the folder where the project execution file is located.
- Dynamically load terasic_pcie_qsys.so in C/C++ program. To load the terasic_pcie_qsys.so, please refer to the PCIe fundamental example below.
- Call the library API to implement the desired application.
2-0-10 8.4 PCI Express Library API
2-0-11 8.5 PCIe Reference Design – Fundamental
- Download Batch file: test.sh
- Linux Application Software folder : linux_app, includes
- PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL
- terasic_pcie_qsys.so
- Demonstration Setup
- Install the FPGA board on your PC as shown in Figure8-3.
- Open a terminal and use "cd" command to goto "CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_Fundamental/demo_batch".
- Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable pointing to the Quartus installation path. Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable by tying the following commands in terminal. Replace /home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus to your quartus installation path.
| export QUARTUS_ROOTDIR=/home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus |
- Execute "sudo -E sh test.sh" command to configure the FPGA
- Restart Linux
- Install PCIe driver. The driver is located in the folder:
- Development Tools
- Quartus Prime 18.0 Standard Edition
- GNU Compiler Collection, Version 4.8 is recommend
- Demonstration Source Code Location
- Quartus Project: Demonstrations/PCIe_Fundamental
- C++ Project: Demonstrations/PCIe_SW_KIT/Linux/PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL
- FPGA Application Design
Figure 8-9 shows the system block diagram in the FPGA system. In the Qsys, Altera PIO controller is used to control the LED and monitor the Button Status, and the On-Chip memory is used for performing DMA testing. The PIO controllers and the On-Chip memory are connected to the PCI Express Hard IP controller through the Memory-Mapped Interface.
| Name | Description |
| PCIE_FUNDAMENTAL.cpp | Main program |
| PCIE.c | Implement dynamically load for terasic_pcie_qsys.so library file |
| PCIE.h | |
| TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | SDK library file, defines constant and data structure |
- The PCI express driver is loaded successfully.
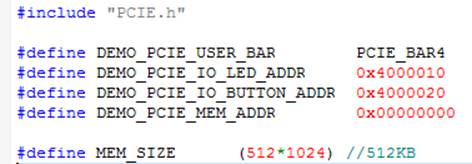
|
| |
2-0-12 8.5 PCIe Reference Design - DDR4
- Download Batch file: test.sh
- Linux Application Software folder : linux_app, includes
- PCIE_DDR4
- terasic_pcie_qsys.so
- Demonstration Setup
- Install DDR4 2400 4GB SODIMM on the FPGA board.
- Install the FPGA board on your PC as shown in Figure8-3.
- Open a terminal and use "cd" command to goto "CDROM/Demonstrations/PCIe_Fundamental/demo_batch".
- Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable pointing to the Quartus installation path. Set QUARTUS_ROOTDIR variable by tying the following commands in terminal. Replace /home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus to your quartus installation path.
| export QUARTUS_ROOTDIR=/home/centos/intelFPGA/18.0/quartus |
- Execute "sudo -E sh test.sh" command to configure the FPGA
- Restart Linux
- Install PCIe driver.
- Make sure the Linux has detected the FPGA Board.
- Goto linux_app folder, execute PCIE_DDR4. A menu will appear as shown in Figure 8-10.
- Development Tools
- Quartus Prime 18.0 Standard Edition
- GNU Compiler Collection, Version 4.8 is recommended
- Demonstration Source Code Location
- Quartus Project: Demonstrations/PCIE_DDR4
- C++ Project: Demonstrations/PCIe_SW_KIT/Linux/PCIe_DDR4
- FPGA Application Design
| Name | Description |
| PCIE_DDR4.cpp | Main program |
| PCIE.c | Implement dynamically load for terasic_pcie_qsys.so library file |
| PCIE.h | |
| TERASIC_PCIE_AVMM.h | SDK library file, defines constant and data structure |
- The PCI express driver is loaded successfully.
| 500px |
| |